728x90
ctrl M : 창 작업창 크기 조절
ctrl + , ctrl - : 폰트 크기 조절
ctrl D : 한줄 삭제
ctrl i : 자동 들여쓰기
src 클릭 ctrl n : 프로젝트 생성
ctrl / : 한줄 주석처리하기
ctrl F11 : RUN
ctrl shift / : /**/주석처리하기
ctrl shift F : 자동 줄맞춤
ctrl shift \ : /**/주석처리하기 해제
Ctrl + Shift + [ :: 화면 세로 분할 단축키
Ctrl + Shift + _ :: 화면 가로 분할 단축키
ctrl alt ↓ : 문장 복사하여 아래에 붙이기
ctrl spacae : 자동완성
ctrl shift o : 자동으로 import
Alt Enter : 현재 파일 위치 open
블록지정 + Alt ↓ 또는 Alt ↑ : 문장 위아래 이동
Alt Shift M : 메소드 추출
F3 : java API 보기
F6 : 디버깅모드 중단점 이동 , 다음 이동
F8 : 디버깅 모드 시작 중단
=====================================================================
JDK : 자바에서 제공되는 개발용 라이브러리
JAVA SE : 스탠다드 에디션
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
JRE : 자바 프로그램이 실행되는 환경 8.0 까지 무료
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#java8
JVM : 자바 가상머신, JRE가 설치 되어 있어야 한다.
=====================================================================
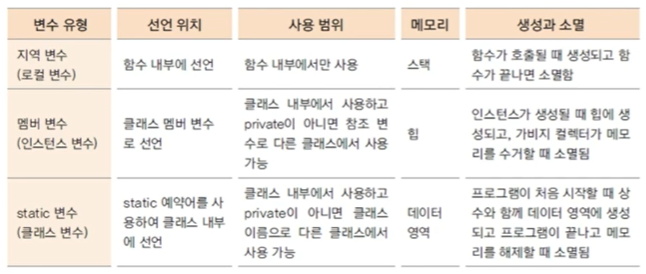
접근 제어자
public : 제한없다.
protected : 같은 패키지 내부 에서만 ok , 상속관계 클래스 ok
(default) : 같은 패키지 내부 에서만 ok
private : 같은 클래스 내부 에서만 ok
=====================================================================
스택 : 지역 변수들이 사용하는 메모리
인스턴스 : new 키워드를 이용하여 클래스를 메모리에 생성한 상태 Student std = new Student();
힙 : 생성된 인스턴스는 동적 메모리에 할당된다.
C , C++ 에서는 사용한 동적 메모리를 프로그래머가 해제 해야함( free() , delete )
자바에서는 가비지 컬렉터가 주기적으로 사용하지 않는 메모리 수거
메서드 : 맴버 변수를 이용하여 클래스 기능 구현한 함수
참조 변수 : 메모리에 생성된 인스턴스를 가리키는 변수
참조값 : 인스턴스 메모리 주소
=====================================================================
생성자 : 반환값 없음 , 클래스의 이름과 동일
필요에 의해 private으로 선언되는 경우도 있다.
기본 생성자 : 클래스에는 반드시 하나 이상의 생성자 존재
★ 클래스에 생성자가 하나도 없는경우에만 컴파일러가 자동 생성
Student studentLee = new Student(); <=> public Student() {}
=====================================================================
this :
- 인스턴스 자신의 메모리를 가리킴
1. Student studentLee = new Student( 11 );
2. public class Student {
public int studentNumber;
public Student( int studentNunber ) {
this.studentNumber = studentNumber;
}
}
- 생성자에서 또다른 생성자를 호출
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person() {
//super() :: 상속된경우 상위 클래스 호출( 생략가능 )
this("홍길동", 1); ::this() 이전에 다른 statement를 쓸 수 없음
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
- 자신의 주소를 반환
public class Person {
public Person getPerson() {
return this; :: 자신의 주소를 반환함
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person pr = new Person();
Person prType = pr.getPerson();
System.out.println(prType);
}
}
=====================================================================
오버로딩 : 기존에 없는 새로운 메서드를 정의
int add( int a , int b){}
int add( int a , long b){}
오버 라이딩 ( 덮어쓰다 )
상속받은 메소드의 내용만 변경
조상보다 접근 제어자( public , private)좁은 범위로 안됨
예외 선언시 조상의 메소드 보다 많이 선언 할 수 없다.
class Parent { void parentMethod() throw IOException , SQLException {} }
class Child extends Parent { void parentMethod() throw IOException {} }
=====================================================================
인스턴스 : ClassName d1 = new ClassName();
- 일반 메소드 내에서 인스턴스 변수(iv) 사용가능
static :
- ClassName.method(); :: new로 객체 만들지 않고 호출 가능
- 프로그램이 메모리에 로딩될때 할당
- static 메소드 내에서 인스턴스변수(iv) 사용불가
public static int serialNum = 1000;
private int employeeId;
public static int A1(){
int a = serialNum; :: 가능
int b = employeeId; :: 불가
return a;
}
=====================================================================
싱글톤 패턴
프로그램에서 인스턴스가 단 한 개만 생성되어야 하는 경우 사용하는 디자인 패턴
static 변수, 메서드를 활용하여 구현 할 수 있음
private static Company instance = new Company();
private Company() {} // 생성자는 private으로 선언
public static Company getInstance() {
return instance == null ? new Company() : instance;
}
===================================================================== for( 변수 : 배열 ) {}
기본 자료형 배열 ( 빈 index 0.0)
int[] arr = new int[3];
int[][] arr = new int[3][5];
int[] arr = new int[]{ 1,2,3 }
int[][] arr = new int[3][5]{ {1,2,3} , {1,2,3,4,5} };
int[] arr = { 1,2,3 }
int scount = 0;
double[] darr = new double[5];
darr[0] = 1.1; scount++;
darr[1] = 2.1; scount++;
darr[2] = 3.1; scount++;
double total = 1;
for( int i = 0 ; i < scount ; i++ ) {
total *= darr[i];
System.out.println(total); :: 결과 0
}
객체 자료형 배열 ( 빈 index null )
Book[] library = new Book[5];
library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1","홍길동1");
library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2","홍길동2");
for(Book book : library ) {
System.out.println(book);
}
배열 복사
배열의 주소를 그대로 복사한다.
원본배열 , 어디부터? , 복사배열 , 어디부터? , 총 몇개?
System.arraycopy(library, 0, copyLibrary, 0, 4);
Book[] library = new Book[5];
Book[] copyLibrary = new Book[5];
library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1","홍길동1");
library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2","홍길동2");
System.arraycopy(library, 0, copyLibrary, 0, 4);
library[0].setAuthor("박원서");
library[0].setTitle("나무");
for(Book book : library ) {
System.out.println("원본" + book);
}
for(Book book : copyLibrary ) {
System.out.println("복사본" + book); // 주소도 똑같이 복사됨.
}
ArrayList
- 주요 메서드( E는 요소의 자료형 )
boolean add( E e ) 요소 하나 추가
int size() 배열에 추가된 요소 전체 개수를 반환
E get(int index) 배열의 index 위치에 있는 요소값 반환
E remove( int index ) 배열의 index 위치에 있는 요소값을 제거하고 그 값 반환
boolean isEmpty() 배열이 비어있는지 확인
=====================================================================
상속 : - class Child extends Parent {}
- 여러개의 클래스로부터 상속 받을수 없다.
- 하위 클래스가 상위 클래스의 속성과 기능을 확장
- 하위 클래스가 생성이 될때 항상 상위 클래스가 먼저 생성 된다.
1. 하위 클래스에서 명시적으로 상위 클래스 생성자를 호출하지 않으면 super() 호출
(super() 는 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자를 호출)
public Child () {
super() :: 생략 가능
2. 상위 클래스에 기본 생성자가 없는경우 하위 클래스 에서 super를 이용하여
명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출 해야 한다.
public Parent ( int customerID , String customerName ) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName = customerName;
public Child (int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
=====================================================================
형변환( 업캐스팅 )
- 상위 클래스로 변수를 선언하고 하위 클래스의 생성자로 인스턴스를 생성
Parent vc = new Child( 123 , "no-name" );
vc. ~~ << Parent 것만 사용 가능
- 상위 클래스 타입의 변수에 하위 클래스 변수가 대입
Child vc = new Chile();
addChild( vc ); / int addChild( Parent pp ){}
형변환(다운캐스팅)
- Parent parent = new Child(); :: 명시적 형변환 필수
Child child = (Child)parent;
- instancof는 해당 클래스가 자기집이 맞는지 확인해 주는것
1. parent instanceof Parent : 부모가 본인집을 찾았으니 true
2. child instanceof Parent : 자식이 상속받은 부모집을 찾았으니 true
3. parent instanceof Child : 부모가 자식집을 찾았으니 false
4. child instanceof Child : 자식이 본인집을 찾았으니 true
ArrayList<Animal> animalList = new ArrayList<>();
animalList.add(new Human());
animalList.add(new Tiger());
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.testDownCasting(animalList);
public void testDownCasting( ArrayList<Animal> list ) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Animal animal = list.get(i);
if( animal instanceof Human ) {
Human human = (Human)animal;
human.readBook();
}else if( animal instanceof Tiger ) {
Tiger tiger = (Tiger)animal;
tiger.hunting();
}else {
System.out.println("알수없음");
}
}
}
===================================================================== 에너테이션
@Overriding 재정의 메서드
@Functionalinterface 함수형 인터페이스
@Deprecated 이후 사용되지 않을수 있는 변수, 메서드
@SuppressWarnings 특정 경고가 안나오게
=====================================================================
다형성( polymorphism )
- 하나의 코드가 여러 자료형으로 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Animal{
public void move() { System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다."); }
}
//_________________________________________________
class Human extends Animal{
@Override
public void move() { System.out.println("사람이 두발로 걷습니다."); }
public void readBook() { System.out.println("사람이 책을 읽어요"); }
}
//_________________________________________________
class Tiger extends Animal{
@Override
public void move() { System.out.println("호랑이가 네발로 걷습니다."); }
public void hunting() { System.out.println("호랑이가 사냥을 해요"); }
}
//_________________________________________________
public class AnimalTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal nHuman = new Human();
Animal nTiger = new Tiger();
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.moveAnimal(nHuman);
test.moveAnimal(nTiger);
System.out.println("=============");
ArrayList<Animal> animalList = new ArrayList<>();
animalList.add(new Human());
animalList.add(new Tiger());
for ( Animal ani : animalList ) { ani.move(); }
}
public void moveAnimal( Animal animal ) { animal.move(); }
}
=====================================================================
absract - new인스턴스화 할수 없고, 상속하여 구현
추상 클래스 : public abstract class Computer
추상 메서드를 포함한 클래스
추상 메서드 : public abstract void display();
내용이(구현부) 없는 메서드
템플릿 메서드 패턴 : final로 선언하여 재정의 못하게함
public abstract class Car {
// 상속받은 자손Class가 추상Class가 아닌경우엔
// 부모의 abstract 메서드를 모두 재정의 하여야 한다.
final int check = 100;
public abstract void drive(); :: 자손은 재정의 필수!
public abstract void stop(); :: 자손은 재정의 필수!
public void startCar() { System.out.println("시동on"); }
public void turnoff() { System.out.println("시동off"); }
final public void run() {
startCar(); drive(); stop(); turnoff();
::반드시 이 순서대로 실행 되야함.
}
}
=====================================================================
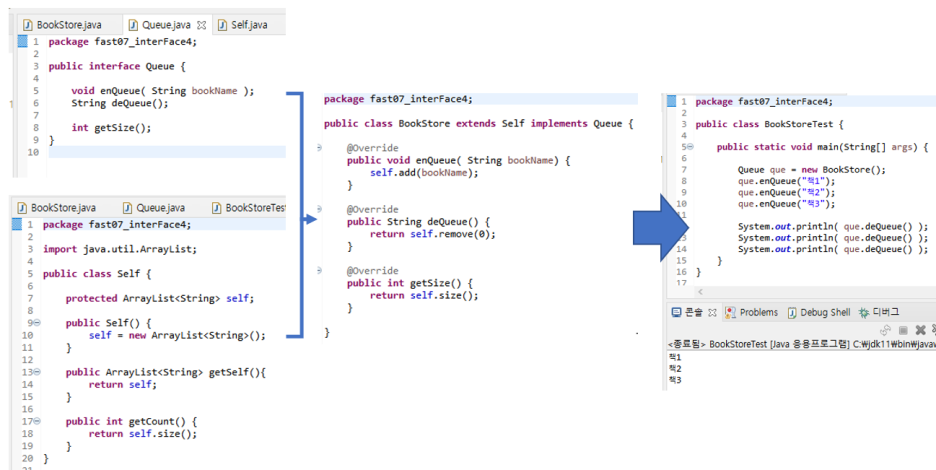
★ 인터페이스( 구현된게 없는 설계도 )
=> 추상 메서드의 집합, 모두 public absract 이고 생략 가능
- default 메서드 > 자바8 이후
구현을 가지는 메서드, 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스들에서 공통으로 사용가능
default void description() { ~~~~ }
- static 메서드 > 자바8 이후
인스턴스 생성과 상관 없이 인터페이스명.메서드 가능
static int total(int[] arr) { ~~ }
- private 메서드 > 9 이후
인터페이스 내부에서만 사용하기 위해 구현하는 메서드
default 메서드, static 메서드 에서 사용
=> 인터페이스 조상은 인터페이스만 가능( object가 최고 조상 아님 )
interface abcInterface{
public static final int name = 1; // 변하지 않는 수(상수) 가능
public abstract String method(); // public abstract 생략 가능
}
=> 다중 상속 가능 :: interface C extends A , B {} // 총돌해도 관계X
=> 구현
:: class C implements A , B { /* 추상 메소드 모두 구현 */ }
:: abstract class C implements A , B { /* 추상 메소드 일부만 구현 */ }
:: class C extends B implements A {} // B 상속받고 , A 인터페이스를 구현하는 C
=> 매개변수가 인터페이스 :: 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스만 가능하다.
=> return 타입이 인터페이스 :: 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스 반환
728x90